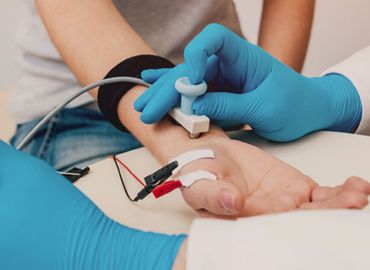
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. It is a non-invasive test that is commonly used to diagnose heart conditions and monitor the heart's function. During an ECG, small electrodes are placed on the patient's chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes detect the electrical impulses generated by the heart and transmit them to a machine that records the information as a series of waves. The ECG provides important information about the heart's rhythm and rate, as well as its structure and function. It can detect abnormalities in the heart's electrical activity, such as irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), heart block, and other conditions that can affect the heart's ability to pump blood effectively.